Quick Start
This guide will walk you through the essential steps to set up the server, create your first dataset and iterate over it.
Installation
pip install lavender-datalavender-data server start --initlavender-data is running on 0.0.0.0:8000UI is running on http://localhost:3000API key created: la-...Save the API key to use it in the next steps.
You can also set the API URL and API key in the environment variables.
export LAVENDER_API_URL=http://0.0.0.0:8000export LAVENDER_API_KEY=la-...Create a dataset
You need a directory containing the shard file(s). It should be flat, containing the shard files only. If the order matters, sort shards by the filename.
Directory/path/to/your/shardset/
- shard.00000.csv
- shard.00001.csv
- …
The directory can be located on a file system or a cloud storage.
# file systemshardset_location = "file:///path/to/the/shardset"
# s3shardset_location = "s3://my-bucket/path/to/the/shardset"
# webshardset_location = "https://example.com/path/to/the/shardset"Use this example shardset if you don’t have any shards yet.
https://docs.lavenderdata.com/example-dataset/images/lavender-data client \ --api-url http://0.0.0.0:8000 --api-key la-... \ datasets create \ --name my_dataset \ --uid-column-name id \ --shardset-location https://docs.lavenderdata.com/example-dataset/images/import lavender_data.client as lavender
lavender.init(api_url="http://0.0.0.0:8000", api_key="la-...")
dataset = lavender.api.create_dataset( name="my_dataset", uid_column_name="id", shardset_location="https://docs.lavenderdata.com/example-dataset/images/",)Wait until the shardset is synced to the server.
lavender-data client \ --api-url http://0.0.0.0:8000 --api-key la-... \ shardsets get \ --dataset-id ds-... --shardset-id ss-...shardset = lavender.api.get_shardset( dataset_id="ds-...", shardset_id="ss-...",)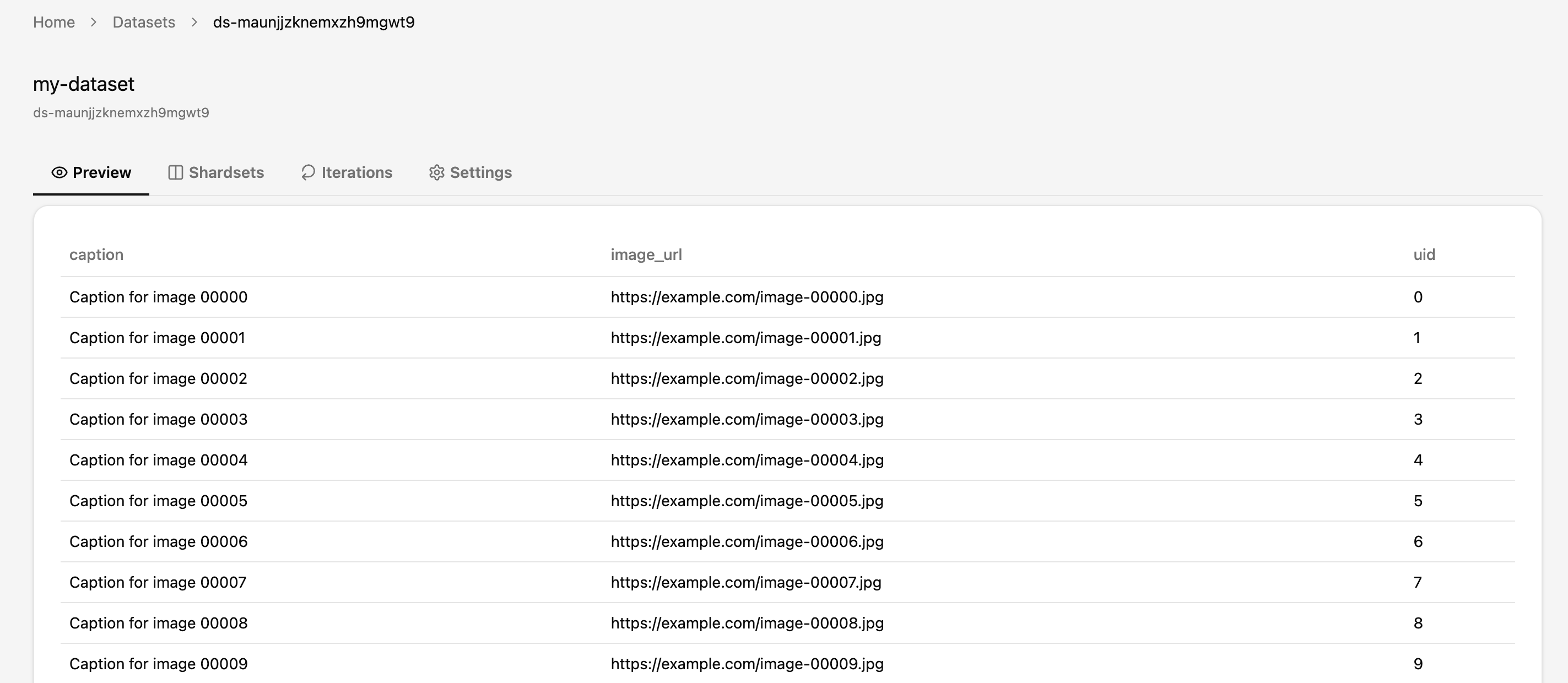
Iterate over the dataset
import lavender_data.client as lavender
lavender.init(api_url="http://0.0.0.0:8000", api_key="la-...")
iteration = lavender.LavenderDataLoader( dataset_name="my_dataset", shuffle=True, shuffle_block_size=10,)
for i in iteration: print(i["id"])You’ve successfully set up Lavender Data, created a dataset, synced data, and iterated over it!